What do you understand by Terraform?
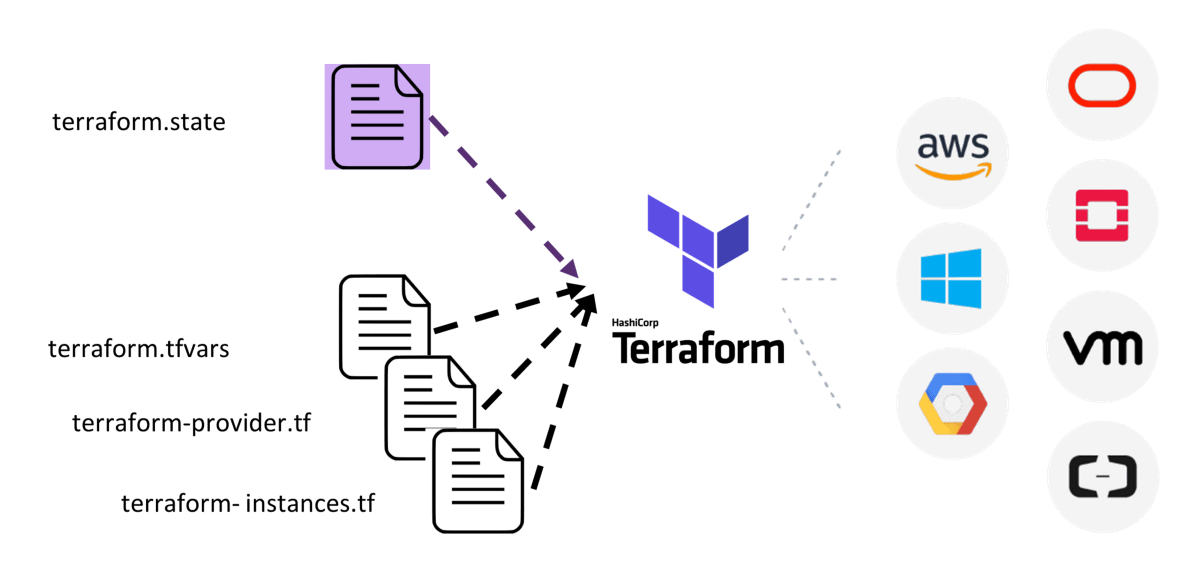
Terraform is an open-source IAC tool created by HashiCorp. It is used to create, update, delete and version your infrastructure on multiple cloud platforms.
Terraform is one of the most popular IAC tools used widely. It allows us to define both cloud and on-premises resources in human-readable configuration files and thereby provision these resources programmatically. The most notable feature of Terraform is that, unlike most IAC tools out there, it is not limited to a single cloud provider. You can use Terraform to run your applications on multiple cloud platforms simultaneously.
In case you are wondering what technologies terraform supports, here is a small list:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Microsoft Azure
IBM Cloud
VMware vSphere
DigitalOcean
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
OpenStack.
It is similar to AWS Cloud Formation in the sense that it is also an “infrastructure as code” tool that allows you to create, update, and version your AWS/any-cloud infrastructure.
What are the reasons to choose Terraform?
Using Terraform for provisioning infrastructure leaves no room for human errors, hence improving the quality, consistency, and efficiency of Cloud and on-prem infrastructure. Terraform uses the language, which is fairly similar to JSON and easy to learn and use. Unlike the other IAC tools offered by cloud providers like Cloudformation for AWS, we can use Terraform with a number of cloud platforms simultaneously. This avoids the need to learn multiple IAC tools and improves the scope of collaboration.
- It can do complete orchestration and not just configuration management (like Ansible and Puppet).
- Has amazing support from almost all the popular cloud providers like AWS, Azure, GCP, DigitalOcean etc.
- Easily manages the configuration of an immutable (dynamic) infrastructure.
- Provide immutable infrastructure where configuration changes smoothly.
- Works on HCL (HashiCorp configuration language), which is very easy to learn and understand.
- Easily portable from one provider to another.
- Easy Installation.
How does Terraform work?
Terraform uses plugins called the Terraform providers to interact with APIs on Cloud Platforms and provision our resources. As an end-user, terraform workflow has three steps.
Write: Author the infrastructure as code.
Plan: Preview changes Terraform will make before applying.
Apply: Provision the infrastructure and apply the changes.
Define IAC?
IAC or Infrastructure as Code allows you to build, change, and manage your infrastructure through coding instead of manual processes. The configuration files are created according to your infrastructure specifications and these configurations can be edited and distributed securely within an organization.
What are the most useful Terraform commands?
Some of the most useful Terraform commands are:
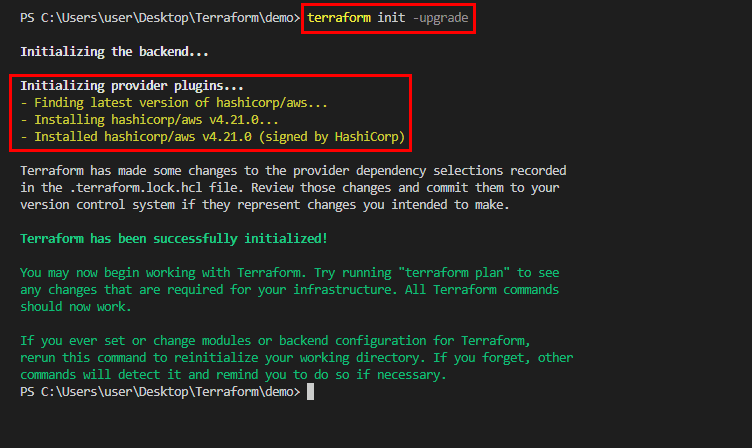
terraform init: initializes the current directory ; Initializes remote backends; downloads providers and remote modules defined in your configuration.
terraform init -upgrade: used to upgrade the existing downloaded providers.
terraform plan: a dry run to see what Terraform will do, it generates the execution plan for the infrastructure creation or updating.
terraform apply: creates or updates the infrastructure after requesting confirmation from the user.
terraform apply –auto-approve: creates or updates the infrastructure; user approval stage is skipped.
terraform destroy: deletes the infrastructure after requesting confirmation from the user.
terraform destroy –auto-approve: deletes the infrastructure; user approval stage is skipped.
terraform fmt: scans the current directory for configuration files and formats them according to the HCP canonical style and format.
terraform fmt –recursive: scans the current directory as well as the sub directories for configuration files and formats them according to the HCP canonical style and format.
terraform show: provides a human-readable output from a state or plan file.
terraform refresh – refreshes the state file
terraform output – views Terraform outputs
terraform graph – creates a DOT-formatted graph
terraform -version of the command to identify the version which we are running
What is Terraform init?
Terraform initialises the code with the command terraform init. This command is used to set up the working directory for Terraform configuration files. It is safe to run this command multiple times.
It is the first command that should be run after writing the new Terraform design
You can use the init command for:
- Installing Plugins
- Installation of a Child Module
- Initialization of the backend
What is Terraform D?
Terraform D is a plugin used on most in-service systems and Windows. Terraform init by default searches next directories for plugins.
Is history the same as it is on the web while using TFS API to provide resources?
Yes, the narration is similar to on the web because UI keeps API as the base. The whole thing that is on the UI is availed during other methods and the API.
Why is Terraform used for DevOps?
Terraform uses a JSON-like configuration language called the HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL). HCL has a very simple syntax that makes it easy for DevOps teams to define and enforce infrastructure configurations across multiple clouds and on-premises data centers.
Define null resource in Terraform.
A terraform null resource is a configuration that runs like a standard terraform resource block but does not create any resources. This may sound like a strange and useless resource, but it can be useful in
various situations to work around limitations in Terraform.
What do you understand by terraform backend?
Each Terraform configuration can specify a backend, which defines two main things:
Where operations are performed
Where the state is stored (Terraform keeps track of all the resources created in a state file)
What do you understand by State in Terraform and what is the benefit of state?
As an IAC tool, terraform should know the current state of configurations and infrastructure under its management. Terraform stores this information in a file called the state file.
The Terraform State allows Terraform to map real-world resources to your configuration, keep track of metadata, and improve performance when planning changes for complex infrastructures. It is a critical component of Terraform.
Name some major competitors of Terraform.
Some of the top competitors and alternatives to Terraform are Azure Management Tools, Morpheus, CloudHealth, Turbonomic, and CloudBolt.
Explain the uses of Terraform CLI and list some basic CLI commands?
The Terraform Command-Line Interface (CLI) is used to manage infrastructure and interact with Terraform state, configuration files, providers, etc.
Here are some basic CLI commands:
terraform init – prepares your working directory for other commands
terraform destroy – destroys the previously-created infrastructure
terraform validate – check whether the configuration is valid
terraform apply – creates or updates the infrastructure
terraform plan – shows changes needed by the current configuration
What are modules in Terraform?
A jug for numerous resources that are used jointly is known as a module in Terraform. The root module includes resources mentioned in the .tf files and is required for every Terraform.
What is a Private Module Registry?
A Private Module Registry is a feature from Terraform Cloud that allows you to share Terraform modules across the organization. You can enforce rules or “sentinel policies” on the registry that specify how members of your organization can use the modules.
Is Terraform usable for an on-prem infrastructure?
Yes, Terraform can be used for on-prem infrastructure. As there are a lot of obtainable providers, we can decide which suits us the best. All that we need is an API.
Does Terraform support multi-provider deployments?
Yes, multi-provider deployments are supported by Terraform, which includes on-prem like Openstack, VMware, and we can manage SDN even using Terram too.
How is duplicate resource error ignored during terraform apply?
We can try the following options:
Delete those resources from the cloud provider(API) and recreate them using Terraform
Delete those resources from Terraform code to stop its management with it
Carry out a terraform import of the resource and remove the code that is trying to recreate them
Name all version controls supported by Terraform
The supported version controls are:
Azure DevOps Services
Azure DevOps Server
Bitbucket Server
Bitbucket Cloud
Gitlab EE and CE
Gitlab.com
GitHub Enterprise
GitHub.com (OAuth)
GitHub.com
What are provisioners and some of the built-in provisioners available in Terraform?
Provisioners are Terraform resources used to execute scripts as a part of the resource creation or destruction.
There are two types of Provisioners in Terraform:
local-exec: Invokes a script on the machine running Terraform.
remote- exec: Invokes a script on a remote resource after it is created.
Provisioners are only meant to be used as a last resort in Terraform.
Here is the list of built-in provisioners in Terraform:
Salt-masterless Provisioner
Remote-exec Provisioner
Puppet Provisioner
Local-exec Provisioner
Habitat Provisioner
File Provisioner
Chef Provisioner
What is the external data block in Terraform?
Just like the local-exec provisioner, external data bock can be used to run scripts on machines running Terraform. The difference between a provisioner and the external data block is that the scripts in the external data block can return data in JSON format, whereas provisioners cannot return any outputs. It is important to note that external data blocks are also meant to be a last resort and should not be used if there is a better alternative.
Which command destroys Terraform managed infrastructure?
The given command is used for this purpose:
terraform destroy [options] [dir]
Tell us about some notables Terraform applications.
The applications of Terraform are pretty broad due to its facility of extending its abilities for resource manipulation. Some of the unique applications are:
Software demos development
Resource schedulers
Multi-cloud deployment
Disposable environment creations
Multi-tier applications development
Self-service clusters
Setup of Heroku App
What are the components of Terraform architecture?
The Terraform architecture includes the following features:
Sub-graphs
Expression Evaluation
Vertex Evaluation
Graph Walk
Graph Builder
State Manager
Configuration Loader
CLI (Command Line interface)
Backend
Define Resource Graph in Terraform.
A resource graph is a visual representation of the resources. It helps modify and create independent resources simultaneously. Terraform establishes a plan for the configuration of the graph to generate plans and refresh the state. It creates structure most efficiently and effectively to help us understand the drawbacks.
What is a provider in Terraform and who maintains them?
Providers in Terraform are plugins that allow Terraform to interact with cloud providers, SaaS providers, and other APIs. For example, if we plan on using Terraform to provision infrastructure on AWS, we will need to declare an AWS provider in our configuration files.
Providers are distributed separately from Terraform itself. As a Terraform user, anyone can develop their own providers. There are some standard providers that are maintained explicitly by Hashicorp.
What is Sentinel?
Sentinel is a policy as a code tool used to enforce standard configurations for resources being deployed by Terraform. It can be used by organizations for compliance and governance purposes.
What are policies and can you provide a few examples where we can use for Sentinel policies?
A policy can include imports which enable a policy to access reusable libraries, external data and functions. Terraform Cloud provides four imports to define policy rules for the plan, configuration, state, and run associated with a policy check.
Sentinels are a powerful way to implement a variety of policies in Terraform. Here are a few examples:
Enforce explicit ownership in resources
Restrict roles the cloud provider can assume
Review an audit trail for Terraform Cloud operations
Forbid only certain resources, providers, or data sources
Enforce mandatory tagging on resources
Restrict how modules are used in the Private Module Registry
What are the various levels of Sentinel enforcement?
Sentinel has three enforcement levels – advisory, soft mandatory, and hard mandatory.
Advisory – Logged but allowed to pass. An advisory is issued to the user when they trigger a plan that violates the policy.
Soft Mandatory – The policy must pass unless an override is specified. Only administrators have the ability to override.
Hard Mandatory – The policy must pass no matter what. This policy cannot be overridden unless it is removed. It is the default enforcement level in Terraform.
How to Store Sensitive Data in Terraform?
Terraform requires credentials to communicate with your cloud provider’s API. But most of the time, these credentials are saved in plaintext on your desktop. GitHub is exposed to thousands of API and cryptographic keys every day. Hence, your API keys should never be stored in Terraform code directly. You should use encrypted storage to store all your passwords, TLS certificates, SSH keys, and anything else that shouldn’t be stored in plain text.
What is Terragrunt, and what are its uses?
Terragrunt is a thin wrapper that provides extra tools to keep configurations DRY, manage remote state and work with multiple Terraform modules. It is used for:
Working with multiple AWS accounts
Executing Terraform commands on multiple modules
Keeping our CLI flags DRY
Keeping our remote state configuration DRY
Keeping our Terraform code DRY
Explain State File Locking?
State file locking is Terraform mechanism in which operations on a specific state file are blocked to avoid conflicts between multiple users performing the same process. When one user releases the lock, then only the other one can operate on that state. This helps in preventing state file corruption. This is a backend operation.
What happens when multiple engineers start deploying infrastructure using the same state file?
Terraform has a very important feature called “state locking”. This feature ensures that no changes are made to the state file during a run and prevents the state file from getting corrupt. It is important to note that not all Terraform Backends support the state locking feature. You should choose the right backend if this feature is a requirement.
What do you understand by a Tainted Resource?
A tainted resource is a resource that is forced to be destroyed and recreated on the next apply command. When a resource is marked as tainted, the state files are updated, but nothing changes on infrastructure. The terraform plan out shows that help will get destroyed and recreated. The changes get implemented when the next apply happens.
What do you understand by modules in Terraform and benefits of using the modules?
A Terraform module is a standard container for multiple resources used together to provision and configure resources. For example, you can create a “VPC module” for your organization that provisions a standard VPC and other resources like Subnets and Internet Gateways. Modules can be shared publically via the Public module registry and privately via the Private Module registry.
Terraform modules allow us to create logical abstraction on the top of a resource set. Using modules allows us to maintain and reuse a standard configuration for resources. They can be versioned and shared with members of your teams to provision resources in a standard way.
What is the Private Module Registry?
A Private Module Registry Terraform Cloud feature allows us to share Terraform modules across our organization.
How can we export data from one module to another?
We can export data from a module by defining output blocks in the module configuration files. This data can then be transferred as a parameter to the destination module.
How can you define dependencies in Terraform?
Terraform has built-in dependency management. Terraform has two kinds of dependencies between resources- implicit and explicit dependencies.
Implicit dependencies, as the name suggests, are detected by Terraform automatically. This is when the output of a “resource A” is used in “resource B”. Terraform automatically detects that “resource B” needs to be created only after “resource A”
Explicit dependencies can be specified in cases where two resources are internally dependent on each other without sharing any outputs. This can be done by using the depends_on parameter in the configuration block.
How to lock Terraform module versions?
A proven way of locking Terraform module version is using the Terraform module registry as a source. We can use the ‘version’ attribute in module of the Terraform configuration file. As the Github repository is being used as a source, we need to specify versions, branch, and query string with ‘?ref’.
What is Terraform Core? Tell us some primary responsibilities of it.
Terraform Core is a binary written statically compiled by using the Go programming language. The compiled binary offers an entry point for the users of Terraform. The primary responsibilities include:
Reading and interpolation of modules and configuration files by Infrastructure as code functionalities
Resource Graph Construction
Plugin communication through RPC
Plan execution
Management of resource state
How can two people using the Terraform cloud can create two different sets of infrastructure using the same working directory?
By using different workspaces. These users can start Terraform runs in two separate workspaces. Each workspace has a state file of its own, so as long as the resources do not overlap, both the users can successfully provision two different sets of infrastructure using the same code.
You have a Terraform configuration file with no resources. What happens when you run the terraform apply command?
Terraform will destroy all the resources. Starting an empty run with terraform apply command is exactly the same as starting the terraform destroy run.
What happens if a resource was created successfully in terraform but failed during provisioning?
This is an unlikely scenario, but when this happens, the resource is marked as tainted and can be recreated by restarting the terraform run.
Which value of the TF_LOG variable provides the MOST verbose logging?
TRACE is the most verbose and the default value of the TF_LOG variable.
How can you import existing resources under Terraform Management?
By using the terraform import command.
Which command can be used to preview the terraform execution plan?
The terraform plan command generates the execution plan of the changes Terraform will do to the infrastructure.
Which command can be used to reconcile the Terraform state with the actual real-world infrastructure?
The terraform apply -refresh-only command is used to reconcile Terraform state with the actual real-world infrastructure. It is the new alternative to the terraform refresh command, which is now deprecated.
Which command can be used to switch between workspaces when using Terraform Cloud?
The terraform workspace select <workspace-name> command is used to choose a different workspace.
Which command is used to perform syntax validation on terraform configuration files?
The terraform validate command is used to verify whether a configuration is syntactically valid and internally consistent.
Which command is used to create new workspaces in the Terraform cloud?
The terraform workspace new <workspace-name> command is used to create a new workspace.
How would you recover from a failed apply in Terraform?
We can save your configuration in version control and commit it before making any changes, and then use the features of your version control system to revert to an earlier configuration if necessary. You must always recommit the previous version code in order for it to be the new version in the version control system.
How will you make an object of one module available for the other module at a high level?
Ab output variable is defined in resource configuration.
Declare the output variable of module_A.
Create a file variable.tf for module B.
Establish the input variable inside this file having the same name as the key defined in module_B.
Replicate the process for making variable available to other modules
What are some of the latest Terraform Azure Provider factors?
The latest versions involve new data resources and Azurem_batch_certificate, which helps in managing the certificate. This resource is used for controlling the prefix in networking. There is fixing of bugs, and azurerm_app_service has also been enhanced.
How will you control and handle rollbacks when something goes wrong?
I need to recommit the previous code version to be the new and current version in my VCS. This would trigger as terraform run, which would be responsible for running the old code. As Terraform is more declarative, I will make sure all things in the code roll back to the old code. I would use the State Rollback Feature of Terraform Enterprise to roll back to the latest state if the state file got corrupted.
How will you upgrade plugins on Terraform?
Terraform providers are distributed separately from the Terraform binary since Terraform v0.10. This allows them to update at different rates while also allowing a larger group of people to collaborate on the providers. This is mostly positive, but it adds a new step for upgrading providers.
Differentiate between Terraform and Cloudformation.
The following points highlight the differences between Terraform and Cloudformation :
- User-friendliness: Terraform works with a variety of Cloud Service Providers, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and others, whereas CloudFormation only works with AWS services. Terraform covers the vast majority of AWS resources.
- Depending on the language: CloudFormation supports JSON and YAML. CloudFormation is now simple to grasp and apply. AWS developers, on the other hand, are not permitted to create CloudFormation templates larger than 51MB. If the size of a template exceeds this limit, the developers must create a layered stack for it.
Terraform, on the other hand, makes use of Hashicorp’s own HCL programming language (Hashicorp Configuration Language). This language is also JSON-compatible. - State-management:
Because CloudFormation is an AWS managed service, it inspects the infrastructure on a regular basis to ensure that it is in good working order. If anything changes, CloudFormation receives a detailed response.
Terraform, on the other hand, stores the state of the infrastructure on the provisioning machine, which can be a virtual machine or a remote computer. Terraform defines the resources it maintains using the state as a map, which is saved as a JSON file.
To summarise, CloudFormation manages Cloudformation’s state by default, preventing conflicting changes. Terraform saves the state to a local disc, making state synchronisation easier. Terraform states can also be saved in storage services such as S3, which is a recommended additional state management strategy. This must be defined on the backend to facilitate and secure management.
- Cost:
The best part is that both of these programmes are completely free. Both of these technologies have sizable online communities that provide a wealth of information and examples. Cloudformation is completely free. Customers only need to pay for the AWS service provided by CloudFormation. Terraform is an open-source application that can be used for free. Terraform, on the other hand, has a paid enterprise version that includes additional collaboration and governance features.
- Integration of Multiple Clouds:
Terraform is the way to go if you want to provide services across multiple cloud platforms. While Terraform can be used with AWS, GCP, Azure, and other cloud providers, CloudFormation is only available on AWS. Cloudformation is not for you if you have multiple cloud installations. If you use AWS resources such as EC2, S3, and so on, you should use Cloudformation.
Differentiate between Terraform and Ansible.
Ansible is a deceptively simple IT automation tool. Configuration management, application deployment, cloud provisioning, ad-hoc job execution, network automation, and multi-node orchestration are all handled by this software. Ansible simplifies complex changes such as zero-downtime rolling updates with load balancers. The following table compares and contrasts Ansible and Terraform:
| Terraform | Ansible |
|---|---|
| Terraform is a tool for provisioning. | Ansible is a tool for managing configurations. |
| It uses a declarative Infrastructure as Code methodology. | It takes a procedural method. |
| It’s ideal for orchestrating cloud services and building cloud infrastructure from the ground up. | It is mostly used to configure servers with the appropriate software and to update resources that have previously been configured. |
| By default, terraform does not allow bare metal provisioning. | The provisioning of bare metal servers is supported by Ansible. |
| In terms of packing and templating, it does not provide better support. | It includes complete packaging and templating support. |
| It is strongly influenced by lifecycle or state management. | It doesn’t have any kind of lifecycle management. It does not store the state. |
Name some major competitors of Terraform?
Answer: Some of them are:
- Packer
- AWS Cloud Formation
- Configuration tools like – Ansible, chef, puppet
- Kubernetes (container management tool)
Give the basic terraform configuration for creating a single EC2 instance on AWS.
This is the Terraform configuration for creating a single EC2 instance on AWS:
provider “aws” {
region = “”}
resource “aws_instance”
“example” {
ami = “”
instance_type = “”
tags {
Name = “example”}
How to launch an EC2 instance using Terraform
— Install Terraform
Select url for terraform download from : https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/downloads
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.3.5/terraform_1.3.5_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_1.3.5_linux_amd64.zip
./terraform -v
mv /home/ec2-user/terraform /usr/bin/ (so that terraform command can be used from anywhere)
— Configure AWS
In AWS go to IAM – create user (terraform) – create group (Terraform-admin) – admin privilege – grab accessid and password
then from the linux box run command : aws configure
AKIASPYN4PQP23PVBGXW
s/yG8d5cKmZBz7MhhiuHeP1sxwGsD8lMklACGn/p
— Install git , download package
yum install git
git clone https://github.com/wardviaene/terraform-course
cd /terraform-course/first-steps
mumbai region: ap-south-1
[root@ip-172-31-2-7 first-steps]# cat instance.tf
provider “aws” {
access_key = “AKIASPYN4PQP23PVBGXW”
secret_key = “s/yG8d5cKmZBz7MhhiuHeP1sxwGsD8lMklACGn/p”
region = “ap-south-1”
}
resource “aws_instance” “example” {
ami = “ami-074dc0a6f6c764218”
instance_type = “t2.micro”
}
terraform init
terraform apply
terraform destroy